If you have been struggling with the annoyance, anxiety, and embarrassment of chronic rhinitis symptoms, you are not alone.
If you have been struggling with the annoyance, anxiety, and embarrassment of chronic rhinitis symptoms, you are not alone.
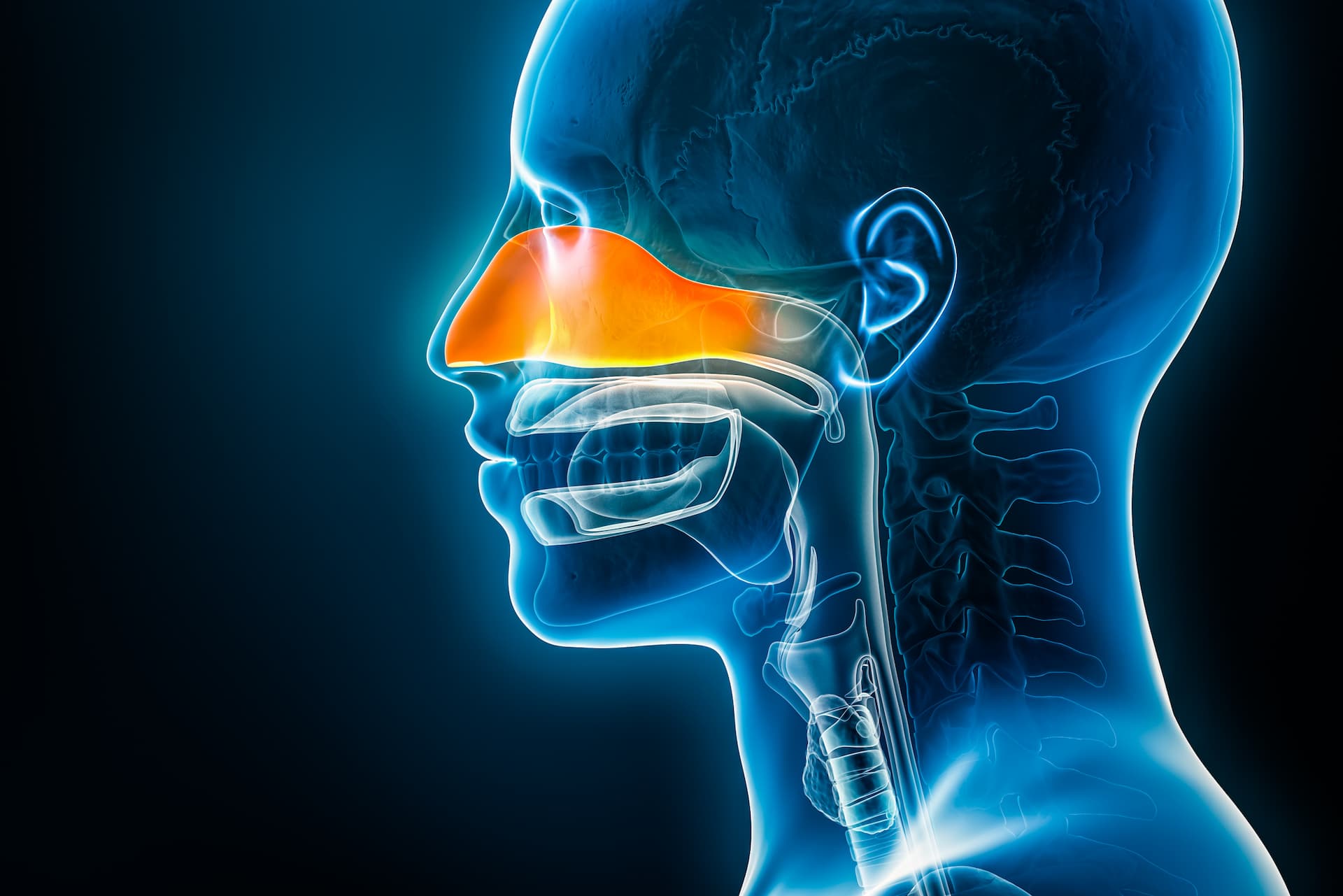
Chronic rhinitis is a condition that affects your nose, causing persistent inflammation and leading to troublesome symptoms like chronic stuffiness, runny nose, or post-nasal drip.
1 in 4 adults experience chronic rhinitis, and 80% of patients with moderate-to-severe rhinitis reported impairment in daily activities. Additionally, individuals with rhinitis are 1.5 to 4.5 times more likely to suffer from comorbid conditions including asthma, eczema, migraine, and depression.
In this article, we will dive deeper into what chronic rhinitis is, the symptoms that can come with it, and the various treatment options that are available, so you can get on the path to breathing better.
Understanding Chronic Rhinitis
 For many patients, chronic rhinitis is caused by overactive posterior nasal nerves that put mucus production into overdrive.
For many patients, chronic rhinitis is caused by overactive posterior nasal nerves that put mucus production into overdrive.
Chronic rhinitis can cause long-lasting irritation and inflammation of the lining of the nasal passages. This inflammation is not caused by allergies, but can be triggered by a range of factors, including infections, long-term health problems, or irritants in the environment.
1. Settipane RA, Charnock DR. Epidemiology of rhinitis: allergic and nonallergic. Clin Allergy Immunol. 2007;19:23-34
2. Ozdoganoglu T, Songu M, Inancli HM. Quali. of life in allergic rhinitis. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2012;6(1):25-39. doi:10.1177/1753465811424425
3. Derebery, J., Meltzer, E., Nathan, R. A., et al. (2008). Rhinitis symptoms and comorbidities in the United States: Burden of rhinitis in America survey. Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery, 139(2), 198–205. h.ps://doi.org/10.1016/j.otohns.2008.05.019
When the nasal passages become inflamed, the blood vessels in the nasal lining dilate, causing swelling and congestion. This congestion can make it difficult to breathe through the nose and may also lead to other symptoms such as nasal itching, post-nasal drip, and reduced sense of smell or taste.
Unlike a common cold which typically resolves within a week or two, chronic rhinitis sticks around for an extended period of time, often lasting for weeks, months, or even years. The symptoms can also come and go year-round.
Symptoms of Chronic Rhinitis
1. Chronic Stuffed-Up Nose
 When you have a chronically stuffed-up nose, it feels like your nasal passages are perpetually blocked or congested. You may find it difficult to breathe through your nose, which can lead to discomfort and frustration. This feeling of congestion may vary throughout the day but remains persistent over time.
When you have a chronically stuffed-up nose, it feels like your nasal passages are perpetually blocked or congested. You may find it difficult to breathe through your nose, which can lead to discomfort and frustration. This feeling of congestion may vary throughout the day but remains persistent over time.
2. Chronic Runny Nose
 Similarly, chronic rhinitis often manifests as a persistent runny nose. Your nose keeps producing mucus, which can trickle down your throat or drip out of your nose, causing annoyance and inconvenience. This constant flow of mucus can also lead to irritation of the skin around the nose.
Similarly, chronic rhinitis often manifests as a persistent runny nose. Your nose keeps producing mucus, which can trickle down your throat or drip out of your nose, causing annoyance and inconvenience. This constant flow of mucus can also lead to irritation of the skin around the nose.
3. Chronic Post-Nasal Drip
 Post-nasal drip is another common symptom of chronic rhinitis. It occurs when excess mucus drips down the back of your throat, leading to throat irritation, coughing, or a feeling of having something stuck in yourExit to page back-end throat. This can cause discomfort and may contribute to bad breath.
Post-nasal drip is another common symptom of chronic rhinitis. It occurs when excess mucus drips down the back of your throat, leading to throat irritation, coughing, or a feeling of having something stuck in yourExit to page back-end throat. This can cause discomfort and may contribute to bad breath.
4. Nasal Irritation
 Many people with chronic rhinitis experience nasal irritation. This sensation can be bothersome and may exacerbate other symptoms such as sneezing or a runny nose.
Many people with chronic rhinitis experience nasal irritation. This sensation can be bothersome and may exacerbate other symptoms such as sneezing or a runny nose.
5. Reduced Sense of Smell or Taste
 Chronic inflammation of the nasal passages can interfere with your sense of smell (olfactory function) and taste. You may notice that you have difficulty smelling strong odors or fully enjoying the flavors of food. This can affect your appetite and overall enjoyment of meals.
Chronic inflammation of the nasal passages can interfere with your sense of smell (olfactory function) and taste. You may notice that you have difficulty smelling strong odors or fully enjoying the flavors of food. This can affect your appetite and overall enjoyment of meals.
6. Fatigue and Sleep Disturbances
 Constant nasal congestion and difficulty breathing can disrupt your sleep patterns, leading to fatigue and daytime drowsiness. This can impact your overall quality of life and productivity. Sleep disturbances may also contribute to mood changes and irritability.
Constant nasal congestion and difficulty breathing can disrupt your sleep patterns, leading to fatigue and daytime drowsiness. This can impact your overall quality of life and productivity. Sleep disturbances may also contribute to mood changes and irritability.
7. Headaches
 Some individuals with chronic rhinitis experience headaches, often due to the pressure and congestion in the sinus cavities. These headaches can range from mild to severe and may worsen during periods of increased nasal congestion. Headaches can interfere with daily activities and may require medication for relief.
Some individuals with chronic rhinitis experience headaches, often due to the pressure and congestion in the sinus cavities. These headaches can range from mild to severe and may worsen during periods of increased nasal congestion. Headaches can interfere with daily activities and may require medication for relief.
Risk Factors
 There are a handful of risk factors that can make you more likely to develop chronic rhinitis. Factors that can increase the likelihood of developing chronic rhinitis include:
There are a handful of risk factors that can make you more likely to develop chronic rhinitis. Factors that can increase the likelihood of developing chronic rhinitis include:
1. Inhaling certain types of polluted air
Smog, exhaust fumes, and tobacco smoke are among the environmental factors that can elevate the risk of chronic rhinitis.
2. Being older than 20 years old
Most individuals affected by chronic rhinitis are above the age of 20. This contrasts with allergic rhinitis, which is more prevalent among individuals younger than 20.
3. Long-term use of nasal sprays or drops
It is advised not to use over-the-counter decongestant drops or sprays containing oxymetazoline (such as Afrin or Dristan) for an extended period. Prolonged usage may result in worsening nasal congestion once the decongestant’s effects wear off – , a phenomenon commonly known as rebound congestion.
4. Pregnancy or menstruation
Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy or menstrual cycles can exacerbate nasal congestion, leading to increased discomfort.
5. Exposure to fumes at work
Certain occupations entail exposure to fumes from various materials, which can initiate chronic rhinitis. Common triggers include chemicals, construction materials, and fumes emanating from compost.
6. Certain medical conditions
Some chronic health conditions, such as diabetes and hypothyroidism (a condition characterized by insufficient thyroid hormone production), can either induce chronic rhinitis or exacerbate existing symptoms.
If you have any of these risk factors and are concerned that you may have chronic rhinitis, please reach out to your local ENT.
Complications of Chronic Rhinitis
Individuals with chronic rhinitis may also have complications that come with the disease. It is important to recognize these risk factors and their association with the condition to maximize treatment.
Chronic rhinitis may be associated with:
1. Nasal polyps
Nasal polyps are soft growths that develop on the lining of the nasal passages. These polyps can also form within the sinuses inside the nose and head. They are caused by inflammation or swelling and are noncancerous in nature. While small polyps may not pose significant issues, larger ones can obstruct nasal airflow, resulting in difficulty breathing.
2. Sinusitis
Sinusitis is characterized by inflammation and swelling of the sinuses. Persistent nasal congestion due to nonallergic rhinitis can increase the likelihood of developing sinusitis over time.
3. Challenges in daily life
Chronic rhinitis may interfere with work, social situations, or academic performance. Individuals may need to take time off during symptom flare-ups or for medical appointments to address their condition.
When to See a Health Care Professional
Now that you’ve read through the explanation, symptoms, risk factors, and complications of Chronic Rhinitis, you may be better equipped to advocate for yourself and reach out to your doctor regarding a diagnosis.
See your doctor if you have experienced any of the following: serious symptoms of chronic rhinitis, no relief from home remedies or store-bought medications, or bad side effects from store-bought medications that require no prescription.
After speaking with your doctor, they may recommend treatment options to get you on route to breathing better. Below we will discuss the potential suggestions that your ENT may pose.
Treatment Options for Chronic Rhinitis
1. Nasal irrigation
Nasal irrigation involves rinsing out your nasal passages with a saline solution. This helps to clear away mucus and irritants, providing relief from congestion and post-nasal drip. Nasal irrigation can be done using a variety of devices, including neti pots, squeeze bottles, or nasal irrigation kits.
2. Nasal corticosteroids
Nasal corticosteroid sprays are commonly used to reduce inflammation in the nasal passages. They can help alleviate symptoms such as nasal congestion, runny nose, and post-nasal drip. Corticosteroids work by reducing swelling and inflammation in the nasal tissues, allowing for easier breathing and improved airflow.
3. Antihistamines
Antihistamine medications work by blocking the effects of histamine, a chemical released during allergic reactions. They can help relieve symptoms such as sneezing, itching, and runny nose associated with allergic rhinitis. Antihistamines are available in both oral and nasal forms and are often used as a first-line treatment for allergic rhinitis.
4. Decongestants
Decongestants come in both oral and nasal forms and work by shrinking swollen nasal tissues, temporarily relieving nasal congestion. Oral decongestants are available over the counter and can provide rapid relief from nasal congestion. Nasal decongestant sprays should be used with caution and for short periods only, as they can cause rebound congestion and other side effects with prolonged use.
5. Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy, which can include treatments such as allergy shots or sublingual tablets, is a long-term treatment option for individuals with severe allergic rhinitis. It involves exposing the body to small amounts of allergens to build up tolerance over time and ultimately reduce allergic reactions. Immunotherapy is often recommended for people who do not respond well to other treatments or who have severe allergies that significantly impact their quality of life.
6. Surgery or In-office Procedure
In cases where chronic rhinitis is caused by structural abnormalities like nasal polyps or a deviated septum, surgical intervention may be necessary to correct the underlying issue and alleviate symptoms. A simple and gentle in-office procedure may also be considered for people who do not want to undergo surgery or may have complications with anesthesia.
7. Lifestyle modifications
Making lifestyle changes can also help manage chronic rhinitis symptoms. This may include avoiding triggers such as allergens, irritants, or pollutants, maintaining good nasal hygiene, and using air purifiers to improve indoor air quality. Other potentially helpful lifestyle modifications include staying hydrated, using humidifiers to add moisture to the air, and avoiding tobacco smoke and other environmental pollutants.
Conclusion
 Chronic rhinitis can significantly impact your daily life, causing persistent nasal congestion, runny nose, post-nasal drip, and other bothersome symptoms. However, with proper diagnosis and treatment, including medication or nasal irrigation, in office treatments, and, in some cases, surgery, symptoms can be effectively controlled, allowing you to breathe better and enjoy a higher quality of life.
Chronic rhinitis can significantly impact your daily life, causing persistent nasal congestion, runny nose, post-nasal drip, and other bothersome symptoms. However, with proper diagnosis and treatment, including medication or nasal irrigation, in office treatments, and, in some cases, surgery, symptoms can be effectively controlled, allowing you to breathe better and enjoy a higher quality of life.
If you suspect you have chronic rhinitis, consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. By working closely with your healthcare provider and following their recommendations, you can find relief from your symptoms and improve your overall well-being.